Human Reproduction
Structure and function of male reproductive system
Human beings reproduce sexually and are viviparous.
In humans, the reproductive phase starts after puberty. It involves:
- Gametogenesis
- Insemination
- Fertilisation
- Implantation
- Gestation
- Parturition
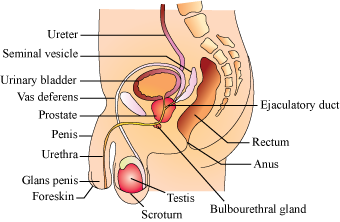
The Male Reproductive System
-
It is located in the pelvic region.
-
It consists of:
-
A pair of testes
-
Accessory glands and ducts
-
External genitalia
-
Testes
.png)
-
Situated within the scrotum, which protects the testes and also helps in maintaining the temperature.
-
Each testis is 4 to 5 cm in length, and 2 to 3 cm in width, and has about 250 compartments called testicular lobules.
-
Testicular lobules have seminiferous tubules which are the sites of sperm formation.
-
Seminiferous tubules are lined by two types of cells:
-
Male germ cells − They undergo meiosis to form sperms.
-
Sertoli cells − They provide nourishment to the germ cells.
-
- Region outside the seminiferous tubules is called the interstitial space, which contains Leydig cells (interstitial cells). The Leydig cells produce androgens.
- Apart from producing sperms, testes also produce a hormone called testosterone. This hormone is responsible for the development of male sex organs like penis and testes. It also brings about secondary sex characteristics in boys during puberty.
Sperm
.png)
- Head: It contains a nucleus, that carries the genetic material. It also contains a large secretory vesicle called acrosome. It secrets hyaluronidase enzyme, that helps in the entry of sperm into the egg by dissolving the ovum wall.
- Neck: It joins the head and middle part.
- Middle Piece: It contains several mitochondria that provide energy (ATP) to the sperm.
- Tail: It helps in the movement of the sperm.
Accessory Ducts and Glands
-
Accessory ducts include:
-
Rete testis
-
Vasa efferentia
-
Epididymis
-
Vas deferens
-
-
The seminiferous tubules open into the vasa efferentia through the rete testis.
-
The vasa efferentia open into the epididymis, which leads to the vas deferens. The vas deferens opens into the urethra along with a duct from the seminal vesicle called the ejaculatory duct.
-
The ejaculatory duct stores the sperms and transports them to the outside.
-
The urethra starts from the urinary bladder, extends through the penis and opens via the urethral meatus.
-
Accessory glands include:
-
A pair of seminal vesicles
-
Prostate gland
-
A pair of bulbourethral glands
-
-
The secretions of these glands make up the seminal plasma, and provide nutrition and a medium of motility to the sperms.
The Female Reproductive System
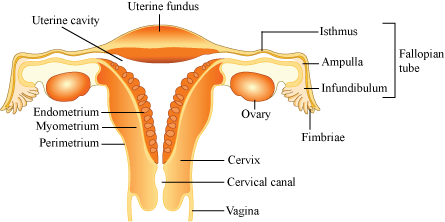
- A pair of ovaries
- A pair of oviducts
- Uterus
- Cervix
- Vagina
- External genitalia
Ovaries
- They are the primary female sex organs. They produce the ovum and other ovarian hormones.
- They are loca…
To view the complete topic, please
